Your employees are innocent against any vichius cyber attack untill you educate them. In order to hold them responsible with their actions. Here is an internal document example to distribute and prepare your employees for some major phishing attack types and increase your company’s security posture.
Introduction
In today’s digital world, cyber threats like phishing and malware are a constant challenge. These attacks can compromise sensitive data, disrupt operations, and damage our company’s reputation. This guide is designed to empower you, our employees, with the knowledge and skills to identify and avoid these threats, protecting both yourself and our organization. Understanding and adhering to cybersecurity practices is not just a best practice; it’s a legal and ethical responsibility.
Why is Cybersecurity Important?
Our company handles sensitive information, including customer data, financial records, and intellectual property. A successful cyberattack can lead to:
- Financial Loss: Direct losses from theft, recovery costs, and legal penalties.
- Reputational Damage: Loss of customer trust and damage to our brand image.
- Operational Disruption: Downtime, lost productivity, and business interruption.
- Legal and Regulatory Fines: Non-compliance with regulations like GDPR can result in significant penalties.
Your Role in Cybersecurity (Legal Responsibilities and Consequences)
Under EU regulations like GDPR and the NIS Directive, our company is obligated to protect personal data and maintain robust cybersecurity measures. As employees, you play a crucial role in upholding these standards.
- Legal Responsibilities: You are expected to handle company data responsibly, adhere to security policies, and report any suspicious activity.
- Consequences of Negligence: Repeated mistakes, such as clicking on phishing links or revealing sensitive information, can lead to disciplinary action, including termination of employment. In some cases, legal action may also be pursued.
- Importance of Training: This training is mandatory and designed to equip you with the necessary knowledge to protect yourself and the company.
Phishing: The Art of Deception
Phishing emails are designed to trick you into revealing sensitive information or installing malware. They often mimic legitimate communications from trusted sources.
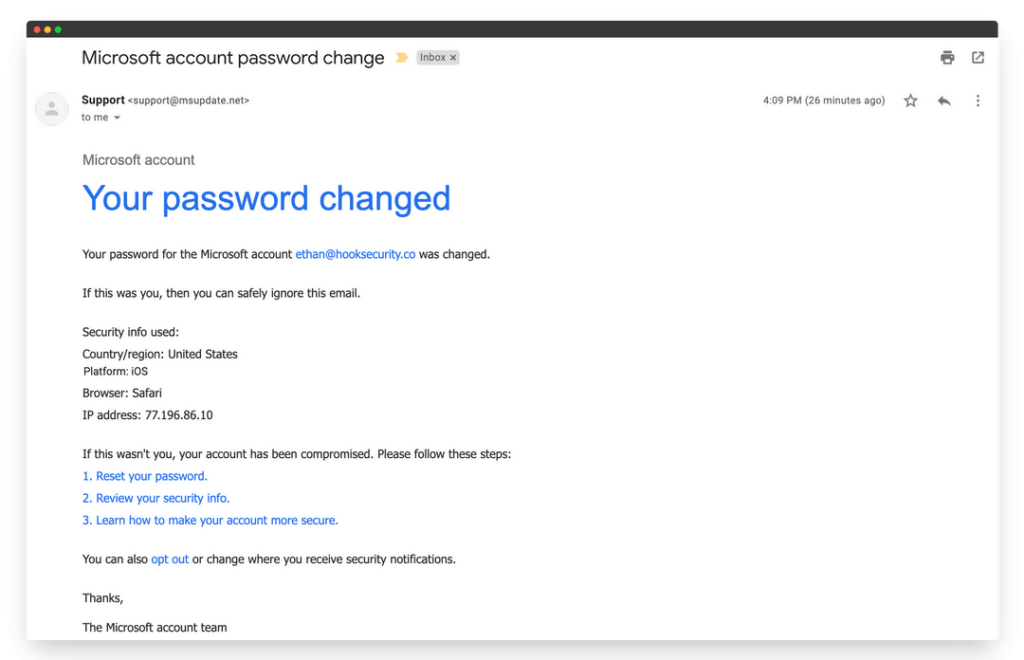
Here 10 Common Phishing Tactics:
| Tactic | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Urgency/Scarcity | Creates a sense of panic, demanding immediate action to avoid negative consequences. | “Your account will be suspended if you don’t update your information within 24 hours.” |
| Authority/Impersonation | Poses as a trusted entity like a bank, government agency, or colleague. | An email appearing to be from your IT department requesting your password. |
| Fear/Threat | Uses threats or intimidation to pressure the recipient into taking action. | “Your computer has been infected with a virus. Click here to remove it.” |
| Greed/Offer | Offers enticing rewards, prizes, or discounts to lure victims. | “You’ve won a free iPhone! Click here to claim your prize.” |
| Social Engineering | Exploits human psychology and trust to manipulate victims. | An email from a “friend” asking for financial assistance. |
| Typosquatting/URL Tricks | Uses slightly misspelled domain names or deceptive URLs to mimic legitimate websites. | “rnicrosoft.com” instead of “microsoft.com” |
| Spoofing | Forges sender addresses to appear as if the email is coming from a trusted source. | An email appearing to be from your CEO but with a slightly different email address. |
| Personalization | Uses personal information to make the email seem more legitimate and targeted. | An email addressing you by name and referencing your job title or department. |
| Attachments | Contains malicious attachments that, when opened, can install malware. | A seemingly harmless invoice or resume in a Word document. |
| Link Manipulation | Links that appear legitimate but redirect to malicious websites. Hovering over links reveals the true destination. | A link that says “Click here to log in” but points to a suspicious URL. |
Malware: The Silent Intruder
Malware (malicious software) is designed to harm your computer or steal your data.
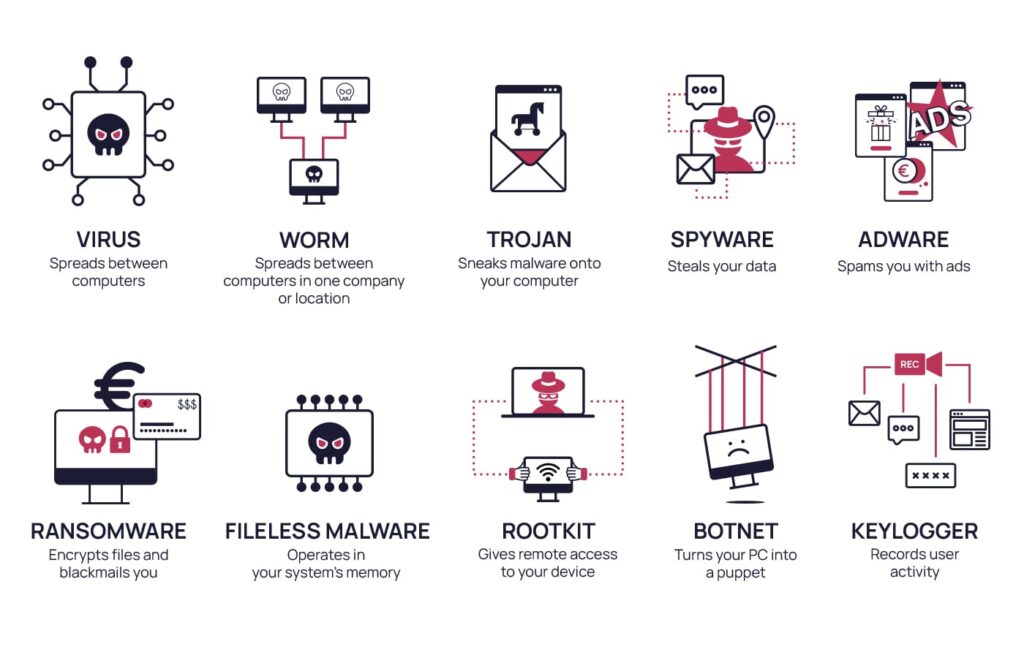
10 Signs Your Computer Might Be Infected:
| Sign | Description |
|---|---|
| Slow Performance | Programs take longer to load, and the computer becomes sluggish. |
| Frequent Crashes | The system freezes, crashes, or displays error messages unexpectedly. |
| Pop-ups and Ads | Excessive pop-up windows or unwanted advertisements appear on the screen. |
| Unusual Activity | Programs launch on their own, files are deleted or modified without your knowledge, or strange network activity is observed. |
| Browser Changes | Your homepage or search engine changes without your consent, or new toolbars appear in your browser. |
| Disabled Security | Your antivirus software or firewall is disabled or stops functioning. |
| Increased Network Traffic | Unusually high network activity, even when you’re not actively using the internet. |
| Missing Files | Files or folders disappear without explanation. |
| Strange Error Messages | Unusual or cryptic error messages appear on the screen. |
| Unauthorized Access | Accounts are accessed without your knowledge, or passwords are changed. |
Export to Sheets
Accessibility Considerations in Phishing:
Phishers may exploit accessibility features to target vulnerable individuals:
- Large Font Sizes/High Contrast: Used to target individuals with visual impairments.
- Screen Reader Compatibility: Phishing emails may be designed to be easily read by screen readers, potentially targeting blind or visually impaired users.
EU Regulations and NIST Framework Alignment:
This guide aligns with EU regulations (GDPR, NIS Directive) by emphasizing data protection and cybersecurity best practices. It also incorporates elements of the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, focusing on:
- Identify: Understanding and managing cybersecurity risks.
- Protect: Implementing safeguards to prevent cyberattacks.
- Detect: Identifying and detecting cybersecurity events.
- Respond: Taking action to contain and mitigate the impact of cyberattacks.
- Recover: Restoring normal operations after a cyberattack.
What to Do If You Suspect a Phishing Email or Malware Infection:
- Do NOT click on any links or open any attachments.
- Report the email to your IT department immediately.
- If you suspect your computer is infected, disconnect it from the network.
Report any suspicious phshing atempt to your Security Departement!
Conclusion
By understanding the tactics used in phishing attacks and the signs of malware infection, you can play a critical role in protecting our company’s digital assets. Remember, vigilance and responsible online behavior are essential for maintaining a secure and productive work environment. Your cooperation in adhering to these guidelines is crucial for our collective security and compliance with legal obligations.